Inflation vs Wage Growth: Are You Falling Behind?
Inflation and wage growth are at odds in today’s economy. Learn how rising prices affect your earnings and what you can do to stay ahead financially.

AFFILIATE DISCLOSURE:
This article contains affiliate links. We may receive a commission for purchases made through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products and services we believe will genuinely help you achieve your financial goals.
Introduction: The Battle Between Inflation vs Wage Growth
In recent years, many individuals have noticed something unsettling: their paycheck doesn’t seem to stretch as far as it once did. Whether it’s the rising cost of groceries, gasoline, or housing, prices are climbing faster than the pay raises many workers receive. This phenomenon has left millions wondering: are we falling behind in the fight between inflation and wage growth?
As inflation continues to rise, it erodes purchasing power—meaning the same amount of money buys fewer goods and services. On the other hand, wage growth has been sluggish, and many workers have seen their salaries barely keep up with the rising costs of living. In this post, we’ll break down the relationship between inflation and wage growth, how it affects you, and what you can do to stay financially strong in the face of these challenges.
Understanding Inflation and Wage Growth
What Is Inflation?
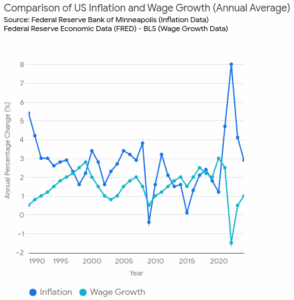
Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, eroding purchasing power. It means that the money you earn today will buy less than it did a year ago. In the U.S., inflation is often measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which tracks the cost of a basket of goods and services over time. A high inflation rate means a significant increase in prices, while a low rate means prices are rising slowly or not at all.
As of 2023, the CPI showed inflation at approximately 6.5%, an alarming rate compared to historical averages. This marked a sharp increase from the relatively low inflation rates seen in the previous decade. Inflation affects virtually every aspect of the economy, from the cost of everyday necessities to long-term investments and savings. It’s a crucial indicator to track, especially when compared to your wage growth. Learn more at Investopedia – What is the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Federal Reserve – Inflation
What Is Wage Growth?
Wage growth refers to the rate at which wages or salaries increase over time. Ideally, wages should rise in tandem with inflation, allowing workers to maintain their purchasing power. However, if wage growth lags behind inflation, workers experience a reduction in their real income—what they can actually afford to buy.
In the U.S., wage growth has been relatively sluggish in recent years, especially when compared to the rising costs of living. For instance, in 2023, the average wage growth rate was approximately 4.5%, whereas inflation was pushing around 6.5%. This means that for many workers, their real income was effectively shrinking, making it harder to cover expenses and save for future goals.
Why Is This Relationship Important?
The interaction between inflation and wage growth is critical because it directly impacts your financial wellbeing. If inflation outpaces wage growth, it can lead to a decrease in your standard of living. Simply put: if your wages don’t grow as quickly as the cost of living, you’re effectively losing money.
Inflation vs Wage Growth: A Closer Look
How Inflation Affects Your Purchasing Power
When inflation increases, the prices of everyday goods and services—such as food, gas, and rent—go up. This can create a significant financial strain, especially for individuals living paycheck to paycheck. If your wage increase doesn’t match the pace of inflation, you may find yourself unable to afford the same things you did the previous year.
For example, in 2023, U.S. inflation was reported at around 6.5%, while average wage growth hovered closer to 4.5%. That’s a significant gap, and it means workers are not keeping up with rising costs.
For instance, grocery prices have risen dramatically, with food prices increasing by 8-10% in some sectors over the last year. This means that for families, the cost of a typical grocery bill can be hundreds of dollars higher annually, creating a strain on their finances. Additionally, higher gasoline prices and housing costs are making it even more difficult for individuals to make ends meet.
The Impact on Savings and Retirement
Inflation doesn’t just affect your day-to-day spending; it can also impact your long-term financial goals. For instance, inflation erodes the value of your savings. If your savings account yields a 1% return, but inflation is 4%, you’re effectively losing money in real terms. The purchasing power of your nest egg is shrinking, making it harder to save for retirement, a home, or your children’s education.
Inflation also impacts the value of fixed-income investments, like bonds. While bonds can offer a steady stream of income, inflation can erode the purchasing power of those payments, reducing the returns investors get over time.
Are You Falling Behind? How to Know If Inflation is Outpacing Your Wage Growth
Understanding the Numbers
To truly understand whether you’re falling behind in the inflation vs wage growth battle, it’s essential to track both metrics. You need to ask yourself: Is my wage increase enough to cover rising prices?
Here’s how you can evaluate your situation:
-
Compare your salary increase to the inflation rate: If your wages are increasing by 3% annually, but inflation is 6%, your real purchasing power is decreasing.
-
Track your spending: Keep a close eye on rising costs in categories such as food, housing, and transportation. If these prices are increasing faster than your wage, it’s time to reconsider your budget or look for ways to increase your income.
-
Focus on long-term financial goals: If your salary is stagnant, focus on building wealth through other means such as investments or starting a side business to make up for lost purchasing power.
Actionable Tips: How to Stay Ahead of Inflation
1. Negotiate Your Salary
If you’re concerned that your wage growth isn’t keeping up with inflation, the first step is to ask for a raise. Many employers are open to negotiating salaries, especially if you can demonstrate your value to the company. Here are a few strategies to increase your chances:
-
Do your research: Use tools like Glassdoor and Payscale to find out the average salary for your position in your area.
-
Prepare your case: Be ready to explain your accomplishments and how they have benefited the company.
-
Show the market rate: If your current pay is lower than the market average, use this information to strengthen your argument.
2. Invest to Combat Inflation
One of the best ways to protect yourself from inflation is by investing. Inflation erodes the value of cash, but investments—especially in assets like stocks, real estate, and bonds—tend to outpace inflation over the long term. Here are a few investment options to consider:
-
Stocks and ETFs: Historically, the stock market has provided returns that outpace inflation.
-
Real estate: Property values generally increase with inflation, providing a hedge against rising prices.
-
Precious metals: Gold and silver are often seen as safe havens during times of high inflation.
3. Reduce Your Expenses
If your salary isn’t keeping up with inflation, reducing your expenses can help you maintain your financial stability. Here are a few strategies:
-
Cut discretionary spending: Consider reducing costs on things like dining out, entertainment, and subscriptions.
-
Shop smarter: Use coupons, look for sales, and buy in bulk to save on everyday expenses.
-
Refinance loans: Lower your interest rates on mortgages, student loans, and credit cards to free up more cash.
4. Diversify Your Income
Building multiple streams of income can provide financial resilience when inflation erodes the value of your paycheck. Here are some ideas:
-
Start a side business: Whether it’s freelance work, selling handmade goods, or offering services, a side business can boost your income.
-
Invest in dividend-paying stocks: These stocks provide a steady stream of passive income.
-
Rent out property: If you have an extra room or property, consider renting it out for additional income.
Internal Links & Resources
-
Who Really Controls the Money? A Look at Central Banks: Understanding how central banks influence the economy and wage growth.
-
The Debt Myth: Why Government Borrowing Isn’t Like a Household Budget: A breakdown of how government spending and monetary policy can affect inflation and wages.
Conclusion: How to Protect Yourself from Falling Behind
As inflation continues to outpace wage growth, it’s crucial to take proactive steps to safeguard your financial future. By negotiating your salary, investing wisely, reducing expenses, and diversifying your income, you can stay ahead of the curve and maintain your purchasing power. While the economic landscape may seem daunting, there are plenty of opportunities to adapt and thrive financially.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How does inflation affect my daily expenses?
Inflation raises the cost of everyday goods and services, making it harder to maintain your standard of living. -
Can I keep up with inflation through wage growth alone?
It’s possible, but it requires constant wage increases that match or exceed inflation. In practice, this can be difficult. -
What’s the best way to protect my savings from inflation?
Invest in assets like stocks, bonds, or real estate that historically outperform inflation. -
How can I measure if my wage growth is enough?
Compare your annual salary increase to the inflation rate to see if you’re maintaining or losing purchasing power. -
Is there a specific industry where wages grow faster than inflation?
Technology and healthcare industries often see faster-than-average wage growth. -
What happens if I don’t adjust my financial plan during inflation?
You may find it more difficult to meet financial goals like saving for retirement or buying a home. -
Are there any government programs to help with inflation?
Programs like Social Security adjustments and certain tax credits may provide relief, but they often don’t keep pace with inflation. -
Should I focus on cutting expenses or increasing income?
A balance of both is ideal, but diversifying your income streams can be more sustainable long-term. -
What’s the best investment to hedge against inflation?
Stocks, real estate, and precious metals are common inflation hedges. -
How can I negotiate a raise to match inflation?
Do research on market rates for your role and present evidence of your contributions and achievements.
Affiliate Disclosure
Affiliate Link Disclosure: TheMoneyQuestion.org may earn a small commission if you make a purchase through one of the links in this article. However, we only recommend products and services that we believe will add value to your financial journey.
Content Disclaimer: The information in this article is for informational purposes only and is not intended to substitute for the advice of a licensed or certified attorney, accountant, financial advisor, or other certified financial professionals. Always seek professional advice before making financial decisions.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links. If you click through and make a purchase, The Money Question may earn a small commission at no additional cost to you. We only recommend products and services we genuinely believe in. See our full disclaimer for details.

Leave a Reply