Why Private Banks Create Most of the Money in the Economy
The popular belief that governments, through their central banks, print and control the money supply is largely a myth. Learn how private banks create money, why it matters for your financial life, and how understanding this can empower your personal finance decisions.

AFFILIATE DISCLOSURE:
This article contains affiliate links. We may receive a commission for purchases made through these links, at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products and services we believe will genuinely help you achieve your financial goals.
Introduction: Who Really Controls Money in Our Economy?
Have you ever wondered where money actually comes from? We tend to think of it as something printed by the government, but the reality is far more complex. In fact, private banks create most of the money circulating in the economy today.
This might sound surprising, but once you understand how it works, it can transform the way you think about money, debt, and even your personal finances. In this post, we’ll dive deep into how private banks create money through the lending process, the implications of this for economic stability, and why it matters to you as a consumer. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of the monetary system and its impact on your financial life.
The Role of Banks in the Economy: More Than Just Lenders
How Banks Work
Banks play a crucial role in the economy, but they’re not just places to deposit your paycheck or take out a loan. Private banks, in particular, are the primary entities responsible for creating the vast majority of money in circulation. How? Through a process called fractional reserve banking.
What is Fractional Reserve Banking?
In simple terms, fractional reserve banking allows banks to lend out most of the money deposited by their customers, keeping only a fraction in reserve. This creates money out of thin air, as loans are made that exceed the actual deposits in the bank’s vaults.
For example:
-
You deposit $1,000 into a bank.
-
The bank is required to keep only 10% (or $100) in reserve, which means it can lend out $900.
-
When the bank loans that $900 to someone else, that money is spent and deposited into another bank.
-
The second bank can now lend out 90% of that deposit, and the cycle continues.
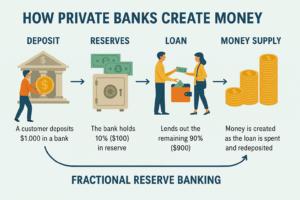
This process of lending and re-lending creates money in the form of credit and debt that circulates throughout the economy. As a result, the actual supply of money in the economy can be many times greater than the amount physically printed by the government.
How Do Private Banks Create Money?
Private banks are not just custodians of money; they are active participants in its creation. Here’s a breakdown of how this happens:
1. Deposits Lead to Loans
When you deposit money into a bank, it doesn’t just sit there. The bank uses your deposit as a source of funds to offer loans to others, and in the process, it creates new money.
2. Money Multiplier Effect
The act of lending leads to more deposits being made, which the bank can then lend out again. This “money multiplier” effect causes the supply of money to grow exponentially. The initial deposit creates more than just a one-to-one increase in money supply.
3. Interest Payments and Debt
The money that banks lend is not free. The borrower must pay interest on the loan. This interest is a form of revenue for the bank, but it also means that the economy is operating on a debt-based system. The more money is created, the more debt there is, and the higher the interest payments.
The Consequences of Private Bank Money Creation
While this system allows for economic growth and provides consumers with access to credit, it also has some serious implications:
1. Debt Levels and Economic Cycles
Because private banks create money through debt, the economy becomes heavily reliant on borrowing. As debt levels increase, the risk of economic downturns also rises. When too many people or businesses default on loans, it can lead to financial crises, like the 2008 recession.
2. Inflation and Asset Bubbles
In some cases, the money created by banks leads to inflation, particularly in asset prices like real estate and stocks. When banks lend excessively, demand for these assets rises, which drives up prices, potentially creating asset bubbles.
3. Limited Control Over the Money Supply
Despite the fact that private banks create most of the money, the government and central banks still try to regulate the supply of money through tools like interest rates and reserve requirements. However, because the vast majority of money is created privately, government control over the money supply is limited.
How Does This Impact Your Personal Finances?
Understanding how private banks create money is not just an academic exercise – it has real-world implications for your financial life:
1. Access to Credit
The availability of credit depends largely on the lending policies of private banks. If banks are reluctant to lend, it can be harder for you to get a loan, whether it’s for a car, home, or business. Conversely, if banks are too eager to lend, it can lead to an oversupply of credit and potential financial instability.
2. Interest Rates
Interest rates are influenced by the central bank, but they are also set by private banks based on market conditions and competition. A low-interest rate environment, which happens when banks have easy access to money, can make borrowing more affordable, but it also fuels debt levels.
3. Inflation and Purchasing Power
As banks create more money through loans, inflation can rise, which erodes the purchasing power of your money. For instance, if more money enters the economy, the cost of goods and services may increase. Understanding this can help you make smarter decisions about savings and investing.
4. Wealth Inequality
The way money is created and distributed can also contribute to wealth inequality. Those who can access loans – often the wealthy – are able to benefit from the rising asset prices that are often driven by bank lending. Meanwhile, those who can’t access credit may find themselves left behind.
Trending Question: Can the Creation of Money by Private Banks Lead to Economic Instability?
Many critics argue that the ability of private banks to create money leads to economic instability. They believe this system can encourage irresponsible lending, creating financial bubbles, and contributing to economic crises. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for understanding why policies like Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) and Sovereign Money Systems have been proposed to reform how money is created and controlled.
1. Modern Monetary Theory (MMT)
MMT suggests that governments, particularly sovereign ones, should issue currency directly and spend freely to finance public services, without worrying about balancing the budget. Proponents of MMT argue that a sovereign money system would reduce reliance on private banks and mitigate the risk of financial instability caused by debt-based money creation.
2. Sovereign Money System
In a Sovereign Money System, only the government would have the authority to create money. Under such a system, private banks would no longer be able to create money through loans, which could significantly reduce the risks of inflation and financial instability.
Internal Links:
-
Who Really Controls the Money? A Look at Central Banks
-
This article provides an in-depth look at central banks and their role in the monetary system, complementing the discussion on private banks’ money creation.
-
-
Modern Monetary Theory: Rethinking Economics and Monetary Reform
-
This post explores alternatives to the current monetary system, including MMT, which proposes changes to the way money is created and managed.
-
-
What the Fed’s Move Means For Your Wallet
-
This post explores the implications of central bank actions on personal finances, linking to the discussion of monetary policy and private banks’ role in creating money.
-
External Links:
-
Federal Reserve – How the Federal Reserve Operates (Federal Reserve official site)
-
This official government site offers a clear explanation of how the Federal Reserve System works, its role in regulating money supply, and its relationship with private banks.
-
-
Bank of England – Money Creation in the Modern Economy (Bank of England)
-
A credible and educational source from the Bank of England that explains how money is created in the modern economy, including the role of private banks in the money creation process.
-
- The Bank of International Settlements (BIS) – Money Creation (BIS official publication)
-
The BIS is an international financial institution that provides in-depth reports and studies on money creation, central banking, and its impact on the global economy. This authoritative resource can add credibility to your post.
-
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Financial Future
Understanding that private banks create most of the money in the economy is a powerful insight into how the financial system works. While this system allows for economic growth, it also introduces risks like inflation, asset bubbles, and increased debt levels.
By becoming aware of how money is created and understanding the broader economic forces at play, you can make more informed decisions about your personal finances. Whether it’s understanding how interest rates impact your loans or recognizing the potential risks of an overheated economy, the more you know, the better equipped you’ll be to navigate the complexities of money.
FAQs: Answering Your Burning Questions on Money Creation
-
What is fractional reserve banking, and how does it create money?
-
Fractional reserve banking is where banks hold only a portion of their customer deposits as reserves and lend the rest to borrowers, thus creating new money in the process. This process is called the money multiplier effect.
-
-
How does private bank money creation affect inflation?
-
The creation of money through loans can lead to inflation, especially if too much money is created relative to the supply of goods and services. The more money that is created through lending, the less each unit of currency is worth.
-
-
Why do private banks create money instead of the government?
-
Private banks have the ability to create money through lending, which has become a standard part of the modern banking system. This contrasts with a system where only the government can issue money.
-
-
Can private bank money creation lead to economic crises?
-
Yes, excessive lending can lead to financial bubbles, excessive debt, and instability in the economy.
-
-
How do central banks regulate the money created by private banks?
-
Central banks regulate the money supply through tools like reserve requirements, interest rates, and monetary policy. By adjusting these controls, central banks can increase or decrease the amount of money and credit available.
-
-
What is the difference between sovereign money and fractional reserve banking?
-
Sovereign money is a system where only the government creates money, while fractional reserve banking allows private banks to create money through lending.
-
-
How can I protect myself from inflation caused by money creation?
-
By investing in assets that tend to hold value during inflationary periods, such as stocks, real estate or commodities (i.e. gold, silver).
-
-
Does the government have control over the money supply?
-
The government, through its central bank, can influence the money supply but doesn’t directly control the vast majority of money in circulation, which is created by private banks. It’s important to note the distinction between control and influence — in most developed countries, central banks operate with a degree of independence from the direct political control of the government.
-
-
What are the risks of a debt-based money system?
-
Risks include financial instability, slower economic growth, asset bubbles, and higher levels of national debt. Higher levels of national debt could lead to limited government fiscal flexibility as more government revenue is directed towards interest payments.
-
-
How can I better manage my finances in a debt-driven economy?
-
By creating a comprehensive budget and focusing on paying down high-interest debt, saving consistently, and investing in a diversified portfolio to protect against inflation. In addition, boosting your income and increasing your financial literacy will put you in a better position to manage your finances.
-
Leave a Reply